
The number of people who at risk of serious health problems due to being overweight is increasing. What is the reason for the growth of overweight people in society? How can this problem be solved?
Содержание:
Introduction
Obesity is a global health problem. Interest in the problem of obesity is growing everywhere. In all the media, we often hear: "Obesity is the epidemic of the 21st century", "Obesity is a global catastrophe". In all Newspapers, websites, magazines, advertisements we see means for weight loss, various diets, methods of weight loss.
But how often do we think about the problem itself? The problem of obesity is not the first century. In the distant past, the ability to store fat was an evolutionary advantage that allowed humans to survive periods of forced starvation. Fat women served as a symbol of fertility and health. They were immortalised on the canvases of many artists, for example, Kustodiev, Rubens, Rembrandt. From the ingenious invention of nature – fat, which in the past had a protective function, now millions of people suffer. In General, this problem is becoming one of the global, affecting all countries. According to who, there are more than 1.7 billion people in the world who are overweight or obese. According to who statistics, the number of obese people worldwide has doubled since 1980. In 2012, more than 40 million children under the age of 5 were overweight or obese.
Therefore, the problem of obesity in our time is becoming more urgent and begins to pose a social threat to people's lives.
What is overweight? General information
Overweight is a chronic metabolic disease that can develop at any age.
Being overweight or fat is having more body fat than is optimally healthy. Being overweight is especially common where food supplies are plentiful and lifestyles are sedentary.
As of 2003, excess weight reached epidemic proportions globally, with more than 1 billion adults being either overweight or obese. In 2013 this increased to more than 2 billion. Increases have been observed across all age groups.
A healthy body requires a minimum amount of fat for proper functioning of the hormonal, reproductive, and immune systems, as thermal insulation, as shock absorption for sensitive areas, and as energy for future use. But the accumulation of too much storage fat can impair movement, flexibility, and alter the appearance of the body.
In most developed countries in Europe, 15 to 25% of the adult population is obese. Recently, there has been an increase in the incidence of obesity in children and adolescents worldwide: in the developed world, 25% of adolescents are overweight and 15% are obese. Overweight in childhood is a significant factor in obesity in adulthood: 50% of children who were overweight at age 6 become obese in adulthood, and in adolescence this probability increases to 80%.
Who views obesity as a global epidemic affecting millions of people. The problem of obesity is becoming more urgent and begins to pose a social threat to the lives of people regardless of their social and professional affiliation, area of residence, age and gender.
Statistics
Obesity, even to a small extent, reduces life expectancy by an average of 4-5 years; if it is pronounced, then life is shortened by 10-15 years. For example, data from the National center for the prevention of chronic diseases and the preservation of health in the United States suggest that about 300 thousand Americans die each year due to diseases caused by obesity.
In General, medical statistics show that an average of 60-70% of fatal cases are associated with diseases, which are based on violations of fat metabolism and obesity.
But in the world, according to 2014 data, more than 1.9 billion adults aged 18 years and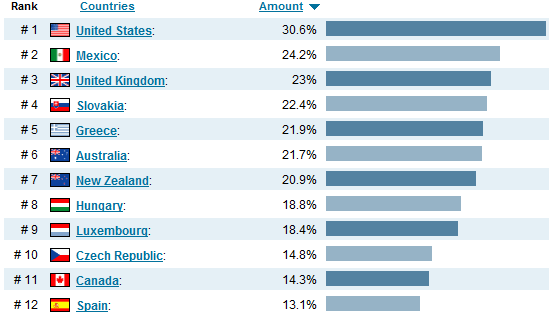 older are overweight. Of that number, more than 600 million people are obese.
older are overweight. Of that number, more than 600 million people are obese.
As for some regions of the world, for example, in almost all European countries, 15-25% of the adult population are obese.
Moreover, in developed countries, the number of overweight people is, according to various estimates, from 35 to 55%, and in some countries (Canada, the United States, Australia, the United Kingdom, New Zealand and Greece) - 60-70%. The share of overweight women in this statistics is about 52%, the share of men - 48%.
Top most obese countries according to The world Health Organisation data from 2013.
It should be noted that in the list of the most obese Nations, Russia occupies a far from leading position, although more than 30% of the working-age population of the country suffers from overweight and obesity. At the same time, 24% of women and 10% of men are prone to obesity in Russia.
Experts are also concerned about the fact that the proportion of overweight people in the world is constantly increasing. So, in the UK over the past 25 years, the number of people exposed to obesity has increased by about 5 times.
Of particular concern is the evidence that the number of overweight children and adolescents has increased globally in recent years. Thus, in developed countries, 25% of the younger generation are overweight, while 15% are obese. The United States, South Africa and Italy were the worst affected by childhood obesity.
And it has long been proven that excess weight in childhood is a high probability of obesity in adulthood. At least, statistics show that 50% of overweight children in 6 years with age begin to gain weight, and excess weight in adolescence increases this probability to 80%.
Given these facts, who in its documents recognises that obesity has already acquired the character of a global epidemic, or pandemic.
Classification of obesity
In different people, adipose tissue is deposited differently, so there are three types of obesity.
- Abdominal (from lat. abdomen - the belly), or Android (from the Greek. andros-male), or upper type of obesity is characterized by excessive deposition of adipose tissue in the abdomen and upper torso. The figure becomes like an Apple. Obesity type "Apple" is more common in men and is the most dangerous to health. It is with this type that such diseases as diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension, heart attacks and strokes develop more often.
- Femoral-gluteal, or lower type of obesity is characterized by the development of adipose tissue mainly in the buttocks and thighs. The figure is shaped like a pear. Obesity type "pear" often occurs in women and is usually accompanied by the development of diseases of the spine, joints and veins of the lower extremities.
- Mixed, or intermediate type of obesity, is characterized by a uniform distribution of fat throughout the body.
Causes and reasons for the growth of overweight people in society
Obesity can occur due to metabolic disease or due to poor nutrition and bad eating habits.
Obesity develops due to a violation of the energy balance of the body, when the energy intake from food exceeds the energy expenditure of the body. Excess calories from what is eaten are used to synthesise fat, which is deposited in fat depots. Gradually increasing fat stores, body weight is steadily increasing.
In recent decades, many countries have improved their living standards, changed their dietary patterns, and increased their consumption of high-calorie, high-fat and low-fiber foods. All this contributes to the consumption of excess energy, and therefore the spread of obesity among more and more people.
Minor, at first glance, "small weaknesses" that a person allows himself, can lead to significant weight gain. For example, if you eat extra drying every day, weight gain will be 1.1 kg per year, 1 tablespoon of mayonnaise-4.8 kg per year.
Weight depends not only on what and how a person eats, but also on how active a lifestyle he leads. As a rule, the modern person leads, basically, a sedentary lifestyle: goes by transport instead of walking; uses an escalator and an Elevator even in those cases when it is possible to do without them; performs work sitting; spends a lot of time in front of the TV and at the computer, which contributes to the growth of body weight and the development of obesity.
Being overweight is generally caused by the intake of more calories (by eating) than are expended by the body (by exercise and everyday activity). Factors that may contribute to this imbalance include:
- Alcoholism
- Eating disorders (such as binge eating)
- Genetic predisposition
- Hormonal imbalances (e.g. hypothyroidism)
- Insufficient or poor-quality sleep
- Limited physical exercise and a sedentary lifestyle
- Poor nutrition
- Metabolic disorders, which could be caused by repeated attempts to lose weight by weight cycling
- Overeating
- Psychotropic medication (e.g. olanzapine)
- Smoking cessation and other stimulant withdrawal
- Stress
- People who have insulin dependent diabetes and chronically overdose insulin may gain weight, while people who already are overweight may develop insulin tolerance, and in the long run develop type II diabetes.
There are also contributing or predisposing factors to obesity:
- Systematic lack of sleep increases the production of hunger hormone (ghrelin) and reduces the production of satiety hormone (leptin), resulting in a person during the day constantly feels hungry. - In stressful situations, the body requires food rich in carbohydrates (e.g., chocolate), which increases the synthesis of endorphins ("hormones of joy"). And if the body "gets hooked" on such a "drug", the absence of a favourite delicacy will already lead to the production of stress hormone. Thus, a vicious circle is formed
- The roots of obesity come from childhood, when parents ask the child to eat a spoon «for grandma» or «for mom». Or make the baby necessarily eat up the portion, even if he does not want to. Sometimes in the family there are certain food traditions (for example, the use of fatty foods), contributing to the development of obesity
- After 40 years, metabolism slows down, so the need for energy costs decreases. However, the habit of eating calorie-rich foods remains. In addition, physical activity tends to decrease with age
- Products with the addition of flavour enhancers (eg, sodium glutamate), dulling the feeling of satiety and enhance the taste sensation. As a result, the brain receives a signal that the food consumed is incredibly tasty, and it wants to absorb more and more
- The habit of eating quickly: glucose from the blood, the overwhelming feeling of hunger, the satiety center does not immediately, so there is overeating
- When eating fast food in the body gets a large number of calories and fats
- Insulin and insulin secretion stimulants
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Genetic factor
- Some diseases, in particular endocrine diseases (hypogonadism, hypothyroidism, insulinoma)
- Psychological eating disorders (eg, psychogenic overeating), leading to eating disorders
- The Prader-Willi Syndrome
- Dysfunction of the hypothalamus
- Neuroleptics (antipsychotics)
- Systemic glucocorticosteroids
- Hormonal contraceptive.
The main cause of obesity in both adults and children is overeating. Chronic overeating leads to disturbances in the work of the appetite center in the brain, and the normal amount of food eaten can no longer suppress hunger to the desired extent. Excess, excess food is utilized by the body and deposited "in reserve" in the fat depot, which leads to an increase in the amount of fat in the body, that is, to the development of obesity.
However, there are many reasons that make a person overeat. Strong excitement can reduce the sensitivity of the saturation center in the brain, and a person begins to take more food without noticing. A similar situation can be the result of a number of psychoemotional factors, such as feelings of loneliness, anxiety, longing, as well as in people suffering from neuroses. In these cases, food seems to replace positive emotions. Many eat heavily before going to bed, sitting in front of the TV, which also contributes to obesity.
Age is essential in the development of obesity, which is why there is even a special type of obesity – age. This type of obesity is associated with age-related impairment of a number of special centers of the brain, including the center of appetite. To suppress feelings of hunger with age requires a greater amount of food. Therefore, imperceptibly for themselves, many people over the years begin to eat more, overeat. In addition, a decrease in the function of the thyroid gland, which produces hormones involved in metabolism, is important in the development of age-related obesity.
The most important factor leading to the development of obesity is physical activity, when even the normal amount of food taken is excessive, since the calories received by the body with food are not burned during exercise, but turn into fat. So the less we move, the less we have to eat in order not to get fat.
The main reason for the development of obesity in modern society is a sedentary lifestyle and the consumption of high-calorie food. Initially, the development of pathology occurs due to imbalance, which is characterised by the amount of energy received from food and its costs by the body. Excess calories that are not fully processed, is transferred into fat. It begins to accumulate in the abdominal wall, in the internal organs, subcutaneous tissue, etc. the Accumulation of fat leads to the appearance of excess pounds and disruption of the functions of many human organs. In 90% obesity is caused by overeating, and only in 5% of cases metabolic disorders.
The influence of overweight on health
The importance of the problem of obesity is determined by the threat of disability of young patients and a decrease in overall life expectancy due to the frequent development of severe comorbidities. These include: type 2 diabetes, arterial hypertension, dyslipidemia, atherosclerosis and related diseases, reproductive dysfunction, gallstone disease, osteochondrosis. Obesity reduces resistance to colds and infectious diseases, dramatically increases the risk of complications in surgical interventions and injuries.
In a number of diseases, obesity is one of the components of the underlying disease. For example, in such endocrine diseases as Cushing's disease, hypothyroidism, insuloma, as a rule, there is obesity. This obesity is called secondary obesity. The doctor finds out the cause of obesity in each individual patient, carrying out a number of special studies, and establishes whether obesity is only associated with a sedentary lifestyle and overeating, or there is secondary obesity.
Obesity significantly reduces life expectancy by an average of 3-5 years with a small excess weight, up to 15 years with severe obesity. In almost two out of three cases, the death of a person comes from a disease associated with a violation of fat metabolism and obesity.
Obesity is a danger to the whole body.
The most often from obesity suffer heart of and vessels, because from-for violations exchange fat evolves atherosclerosis, which leads to raising blood pressure, ischemic disease hearts and so on.
The accumulated fat in the abdominal cavity presses on the diaphragm (the muscle separating the chest and abdomen). As a result, the pressure in the chest and abdominal cavities increases, making it difficult to breathe and work the heart. Liver cells are replaced by fat cells, so all types of metabolism in the body are disrupted: fat, protein, carbohydrate, vitamin. As a result, immunity decreases, hair falls out, nails become brittle, skin diseases develop.
Suffers functionality endocrine organs: evolves diabetes mellitus type II type, have men is declining potency, have women violated menstrual cycle.
People with obesity are more prone to the formation of cancers, especially women (breast cancer is the most common).
Disturbed internal organs: kidneys, gallbladder (often formed stones), develop chronic diseases of the stomach and intestines.
Reduced mental and physical performance, irritability appears, disturbed sleep, patients are more difficult to adapt to changing living conditions, and so on.
Develop diseases of the joints due to excessive load on them. From the stubborn figures of statistics it follows that patients with the third degree of obesity die earlier because of the developed complications (for example, heart attack or stroke).
The social side of the problem
The social significance of the problem of obesity is determined by the threat of disability of young patients and a decrease in overall life expectancy due to the frequent development of development of serious diseases.
Persons suffering from severe obesity, can hardly get a job. Obese people experience discriminatory restrictions on promotion, everyday household inconveniences, restrictions on movement, in the choice of clothing, inconveniences in carrying out adequate hygiene measures; sexual disorders are often observed. Children with excess body weight suffer from bullying.
Modern society provokes unintentional obesity in its citizens, promoting the consumption of high-calorie foods with high fat content, and at the same time, thanks to technological progress, stimulates a sedentary lifestyle. These social and technological factors have contributed to the increasing prevalence of obesity in recent decades.
The world Health Organisation has concluded that the main cause of the obesity epidemic in the world was the lack of spontaneous and active physical activity of the population, combined with excessive consumption of high-calorie fatty foods. Obesity significantly reduces life expectancy on average from 3 to 5 years with a small excess weight, up to 15 years with severe obesity. In almost two out of three cases, the death of a person comes from a disease associated with a violation of fat metabolism and obesity.
In society, the attitude to patients with obesity is often inadequate, at the household level it is believed that obesity is a punished gluttony, punished laziness, so the treatment of obesity is a personal matter. Indeed, the public consciousness is still far from the idea that overweight people are sick people, and the cause of their disease is often not in rampant addiction to food, but in complex metabolic disorders that lead to excessive accumulation of fat and adipose tissue.
Currently, there is an increase in overweight in children and adolescents, which from an early age can affect their social well-being. Social well-being refers to a state associated with social comfort or discomfort, with satisfaction with one's status determined by comparing oneself with other individuals. It is possible to allocate such indicators of social well-being of people with excess weight as: their social adaptation, a subjective assessment of the social position, the General characteristic of interaction with their social environment.
Having analysed the existing sources devoted to this problem, we can come to the following conclusions:
- the Social well-being of people suffering from overweight, largely depends on the opinion of their social environment.
- the social status of such people is influenced by the degree of satisfaction with the place and nature of their activities.
- an Important function is able to highlight the communicative qualities of individuals.
- Most obese individuals understand that the modern market is not ready to accept them.
Very fragmentary, in publications devoted to the problem of obesity, it is said about obesity in the context of a social phenomenon, the topics of social well-being of people suffering from excess body weight are almost not affected. Obesity as a social phenomenon is primarily caused by the problem of acceptance by society of people suffering from obesity.
In England and the United States, obesity is noted more often in women from lower social strata, and pronounced obesity is found in them 2 times more often. Men also have a relationship between social status and obesity. It is a very different situation in India, where obesity has a different meaning: rich men and women are fuller than their less well-off compatriots and obesity is a symbol of well-being.
Solution of the overweight-problem
There are several treatment options for obesity.
- Dietary treatment of obesity
- Bodily exercises
- Psychotherapy
- Medical treatment of obesity
- Preparations of plant origin
- Surgical treatment of morbid obesity.
Dietary treatment of obesity
Obesity can lead to serious diseases. And weight loss is always good for the body, because it is always accompanied by:
- improving the cardiovascular system;
- reducing shortness of breath and swelling;
- the improvement of carbohydrate and lipid metabolism;
- reducing pain in the spine and joints;
- improving overall health.
Getting rid of extra pounds is both simple and very difficult. On the one hand, all the recommendations are commonplace, on the other-they are difficult to comply with. To achieve any result, it is necessary, first of all, to set real, achievable goals and understand that you can not rush. To lose weight without harm to health, you need time. Rapid weight loss will soon lead to its increase again. Reduce weight should be gradually: 0.5-1.0 kg per week, no faster than 3-4 kg per month. Such a slow, gradual weight loss, about 10-15% for 3 months of treatment (example: if your weight is 100 kg, you can lose weight by 10-15 kg), will not only improve health, but also help to keep the achieved result for a long time.
The greatest practical effectiveness in the treatment of obesity is achieved by observing nutrition protocols (diets) with a low content of easily digestible carbohydrates:
- LCHF (Low Carb, High Fat - low-carb high-fat nutrition system)
- The Paleolithic diet
- The ketogenic diet
- MMT diets (mitochondrial metabolic therapy by Dr. Joseph Mercola)
- Keto-carnivore diets
All these nutrition protocols lead to a decrease in the level of insulin in the blood, restoration of insulin resistance to normal levels, and to the transition of the body to the mode of burning its own fat reserves. Often this is accompanied by the restoration of many other parameters of the blood.
This is mainly a diet with a moderate amount of protein (from 1 to 1.5 grams of protein per 1 kilogram of muscle mass per day), an increased content of saturated fats (mainly animal fats, as well as olive and coconut oils, avocado), increased or moderate fiber content (leafy greens, cucumbers, celery, asparagus, etc.), vitamins and other biologically active components, limiting the use of easily digestible carbohydrates:
- Sugar;
- Candy;
- Pastry;
- Bakery and pasta;
- Grain;
- Fruits with high sugar content;
- Vegetables with high starch and sugar content (carrots, potatoes, tomatoes, etc.);
- Dairy products with high lactose content;
- Sugary or high-carbohydrate beverages (juices, carbonated beverages with added sugar, alcoholic beverages);
- Products of deep processing (contain hidden carbohydrates, TRANS fats).
The advantages of these power protocols are the following factors:
- Wide applicability for different ages and different diseases;
- Comfortable diet due to the absence of hunger;
- No surgical intervention.
At the same time, many of these nutrition protocols do not require limiting the caloric content of food, but on the contrary, recommend eating until satiety, so as not to feel hungry. However, the effectiveness of some of them in the treatment of obesity increases significantly when they are combined with various methods of fasting, which are carried by the body much easier than when eating mainly carbohydrate food.
The transition to any nutrition Protocol should be performed under the supervision of a qualified physician. Before switching to a new diet, blood tests should be done, as well as regular monitoring of the necessary parameters on the basis of laboratory tests. For example, due to the high iron content in meat, when choosing a keto-carnivore diet, it is important to take into account the markers of iron in the blood (iron ions in the blood, hemoglobin, ferritin, transferrin).
Bodily exercises
The process of treating obesity is 80% influenced by diet, and 20% influenced by exercise. Recommended types of training: HIIT (eng.) (Interval training), moderate cardio training 2-3 times a week for 20-30 minutes. If there are contraindications, be sure to consult a doctor.
Continued economic growth, the violent pace of industrialisation and urbanisation can minimise the need for activities that require physical effort. Our ancestors did not have to pay for performing physical labor and receiving loads. They were forced to do so by life itself. We, who live in cities, need to pay a considerable amount to visit a modern fitness center or pool, work out or undergo a session of medical procedures. Meanwhile, movement is essential for maintaining the normal structure and function of almost all organs and systems in our body. Its absence without good reasons will sooner or later lead to pathological changes in organs and tissues of the body, to General health problems and early aging.
Numerous epidemiological studies have shown that a sedentary lifestyle is most often associated with an increase in metabolic disorders, in particular, overweight and obesity. An interesting fact is that obesity is bi-directional in reducing physical activity, i.e. lack of exercise leads to weight gain, and it is more difficult for overweight people to initiate physical activity. Thus, the accumulation of excess weight worsens and leads to the formation of a kind of vicious circle. It is the increased energy consumption and reduced physical activity that is responsible for the observed jump in the prevalence of obesity at the present time. It is believed that nutrition has a greater share of risk, because through it we can more easily generate a positive balance of energy than compensate for it then through physical activity.
Psychotherapy
One of the most effective approaches in psychology to work with people who are obese is cognitive behavioural therapy, which most effectively affects the causes that induce a person to overeat. In addition, it makes it possible to adjust some aspects of the quality of life of patients, thereby improving their quality of life. Psychotherapeutic approach to the treatment of obesity is desirable to implement at different levels (family, school, society).
Behavioural therapy methods used in the treatment of obesity are aimed at developing self-control, changing attitudes to nutrition and related habits, the introduction of gradually increasing physical activity and the formation of reliable social support. In controlled trials, it was found that patients to whom these methods were applied were later less likely to gain the same body weight than those to whom other treatments were applied.
Canadian scientists have found that the development of obesity can affect negative relationships with parents. Conversely, a good relationship, in particular, with the father has a positive effect on maintaining a normal weight.
When using diets with calorie restriction of food consumed, as well as diets with a high content of carbohydrates, a person experiences a constant feeling of discomfort, often fails in the fight against obesity due to high levels of insulin in the blood, and may come to the conclusion that psychotherapeutic treatment does not work.
Medical treatment of obesity
Medicines, as a rule, allow to achieve only short-term improvement, but not persistent, long-term effect. If after the termination of the course of medical treatment, the patient has not changed his lifestyle and does not comply with dietary recommendations, then the body weight increases again. Perhaps this is due to the fact that overweight causes irreversible inflammatory processes in the hypothalamus, which disrupt the regulation of adipose tissue. Each drug is selected by the doctor individually:
- Phentermine (adipex-P, fastin, ionamine — amphetamine group) — acts as a neurotransmitter norepinephrine, reducing appetite. May cause nervousness, headache and insomnia;
- Orlistat (xenical) - an inhibitor of pancreatic lipase, approximately 30% reduces the absorption of fat, does not suppress hunger, but can cause incontinence of the chair;
- Metformin-affects the metabolism of carbohydrates, especially shown in obesity associated with diabetes.
- Sibutramine (meridia) is a serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor. The drug acts on the centers of satiety and thermogenesis, which is located in the hypothalamus. The drug is contraindicated in patients with uncontrolled hypertension!
- Fluoxetine (prozac) is an antidepressant used by some specialists to suppress appetite, but there is no information about the long-term effects.
- Lorcaserin (belvik) is an agonist of 5-HT2C receptors, suppresses appetite.
- Bupropion (wellbutrin, ziban) is a reuptake inhibitor of norepinephrine and dopamine and suppresses the appetite.
- The combination of Ephedrine with Caffeine is a sympathomimetic, stimulates alpha-and beta-adrenergic receptors, stimulates the production of norepinephrine. It is widely used in Denmark for the treatment of obesity.
- Topiramate is an antiepileptic drug that reduces body weight through an unspecified mechanism.
- Naltrexone-an opioid receptor antagonist, suppresses cravings for delicious food.
- Liraglutide (victoza, saxenda) is an agonist of the HPP-1 receptor. Presumably, it enhances the action of leptin (saturation hormone) through the suppression of its soluble receptor.
Despite the large number of drugs to treat obesity, almost all of them have been banned by the U.S. food and drug administration because of serious side effects. Five of them are currently approved: orlistat, lorcaserin, phentermine-topiramate, bupropion-naltrexone and liraglutide.
Preparations of plant origin
Along with diet and drug therapy, herbal preparations in the form of tea or other medicines can be used, but it is necessary to know their composition well.
An example of the story of herbal treatment for obesity:
«I was advised different diets, but to comply with a strict diet lacked willpower. Several times I got to the hospital with different sores, the doctors told me that I need to lose weight, then there will be nothing to treat, because all my health problems are from obesity. I wanted to be healthy and take care of my children. I kept trying to regain my normal weight and with it my health. On the advice of friends decided to try, along with separate nutrition herbal tea. To make tea, you need to take 1 teaspoon of cornflower flowers and leaves of the three-leaf watch, 2 teaspoons of starflower grass, St. John's wort grass and oregano grass. All the herbs to chop and mix well. A teaspoon of the resulting collection pour a glass of boiling water (preferably in a thermos), insist 2-3 hours, and then strain. Infusion I take half a glass 2-3 times a day for 30 minutes before meals. I drink the drug courses for 2-3 weeks, then take a break for the same period. When the first time embarked on scales, even somebody-has lost 8 kg for 3 weeks.» - Zagorodny Olga.
Surgical treatment of morbid obesity
As it was found out on the basis of long-term studies, the maximum effect in the treatment of obesity is surgery (bariatric surgery). Only surgical treatment makes it possible to solve this problem completely. Currently, the world's most commonly used three types of surgery for obesity. These three operations have been selected by the long-term evolution of bariatric surgery as giving the maximum effect in terms of weight loss while minimising the level of side effects:
- The longest history has gastric bypass (gastric bypass). It began to be used in the 60s of the twentieth century. This operation is to divide the stomach into two parts — small and large, which are not in contact with each other. To the "small stomach" the small intestine is sewn, so that the food moves along a short path. This operation has two components of action: the volume of the small stomach is about 50 ml., therefore, the patient can not consume food in the same volume, and reduced absorption of nutrients when food moves along the shortened path.
- Gastric banding. The operation consists in the imposition of a silicone ring (gastric bandage) on the border of the esophagus and stomach. The bandage creates an obstacle for the passage of food, thereby stimulating the reflexogenic zone of saturation. All modern bandages are adjustable, that is, their lumen can be controlled depending on the individual situation of the patient. In the modern form, the design of the bandage was proposed by the American surgeon of Ukrainian origin Lubomir Kuzmak.
- Sleeve gastroplasty (Sleeve gastrectomy). The operation is to remove part of the stomach and turn it into a thin long tube - "sleeve". The capacity of the stomach is reduced by about 10 times (up to 150-200 ml.). The mechanisms of action of sleeve gastroplasty in relation to weight loss include the creation of a restrictive effect for the passage of food due to a narrow "sleeve", enhanced activation of farnesoid X-receptors due to an increase in bile acids and a hypothetical mechanism for removing the ghrelin-producing zone (ghrelin — hunger hormone). Sleeve gastroplasty has been used as an independent bariatric surgery since 2004.
In addition to the three described standard operations, many other operations are proposed that are not used as often.
Currently, all bariatric operations are performed laparoscopically (i.e. without incision, through punctures) under the control of a miniature optical system.
It should be noted that operations related to plastic surgery, such as liposuction and abdominoplasty, are not intended to combat obesity, but are a way of surgical correction of local cosmetic defects. Although the amount of fat and body weight after liposuction may decrease slightly, but according to a recent study by British doctors, such an operation is useless for health. Apparently, the damage to health is not subcutaneous, but visceral fat, located in the omentum, as well as around the internal organs located in the abdominal cavity. Previously, there were isolated attempts to do liposuction for weight loss (the so-called megaliposuction with the removal of up to 10 kg of fat), but now it is left as an extremely harmful and dangerous procedure, inevitably giving a lot of severe complications and leading to rough cosmetic problems in the form of roughness of the body surface. Moreover, there is evidence that subcutaneous liposuction (for example, in the abdomen), leads to a compensatory increase in harmful visceral fat. Thus, bariatric surgery rather than plastic surgery is used to combat obesity.
Surgical treatment of obesity has strict indications, it is not intended for those who believe that they just have excess weight. It is believed that indications for surgical treatment of obesity occur at a BMI above 40. However, if the patient has problems such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, varicose veins and problems with the joints of the legs, the indications arise already at a BMI of 35. In recent years, the international literature there are works that have studied the effectiveness of gastric banding in patients with a BMI of 30 and above. Moreover, in February 2011, the US licensing authority FDA decided to allow gastric banding starting at a BMI of 30. However, this permission applies only to one model of bandage-LapBand.
Also, a good method of treatment is to follow the daily routine and avoid stress. An integral part of a healthy lifestyle is the observance of the daily routine. This is especially true of sleep. It is recommended to go to bed no later than 22 hours. You need to sleep at least 8 hours a day. Sleep disorders have a negative impact on the activity of the body, in particular, can contribute to the development of obesity. Stress, depression also negatively affect human health. During experiences, people often begin to consume a lot of food, they have increased appetite, which leads to weight gain.
Society has not yet fully realised the need to create and implement programs to prevent obesity. Of course, such a program is a very expensive thing, but the problem of obesity also costs a lot of money. It should be seen as positive that society has begun to spend money on the creation of programs for the prevention of diseases such as hypertension, insulin-dependent diabetes and coronary heart disease. The pathogenesis of these diseases is very closely intertwined with the pathogenesis of obesity. Obesity is associated with the most common and costly diseases: insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (insd), hypertension, coronary heart disease (CHD), a number of tumors. In humans obesity disrupts the activity of at least nine organ systems.
In countries where educational work on primary prevention is actively implemented and educational technologies are implemented during rehabilitation programs for patients in risk groups (Canada, UK, USA, Finland), the dynamics of reduction of cardiovascular morbidity, the frequency of myocardial infarction and mortality is clearly visible. The main components of rehabilitation programs are preventive training (healthy lifestyle training), physical training and psychological support.
The role of government is critical to achieving long-term positive changes in public health. Governments are primarily responsible for guiding and monitoring the initiation and development of the strategy, ensuring its implementation and monitoring the impact over the long term.
Governments need to ensure that information is correct and balanced, consider measures that provide balanced information to consumers so that they can easily make healthy choices, and ensure that appropriate health promotion and health education programmes are in place. In particular, information for consumers should be prepared taking into account literacy levels, communication barriers and local culture, and it should be understandable for all segments and groups of the population. In some countries, health promotion programmes have been designed to take into account considerations of this kind about diet and physical activity. Some governments have already made a legal commitment to ensure that factual information allows consumers to make well-informed decisions about issues that may affect their health.
Health services, especially primary health care, but also other services (such as social services) can play an important role in preventing obesity. Regular study of basic eating and physical activity habits, combined with simple life-long counseling, can reach a significant portion of the population and prove to be a cost-effective exercise. Identifying specific groups at high risk and identifying measures to meet their needs, including possible pharmacological measures, are important components. Key factors for the implementation of these measures are: the training of health workers, the availability of appropriate guidance and possible incentives.
The issue of global consideration of nutrition and physical activity was also raised in the who/world economic forum report at the joint event "Prevention of noncommunicable diseases in the workplace through diet and physical activity».
Who offers several different methods to set priorities for obesity prevention. All of these approaches have the following common steps:
- Problem identification and needs analysis.
- Identification of possible solutions.
- Assessment and prioritisation of possible solutions.
- Strategy formulation.
When setting priorities, it is important to understand that no single intervention will be able to prevent obesity. The determinants of obesity are complex and diverse, so the solutions must be multifaceted. Depending on the area, region or country, some measures or specific policy options will be more important, relevant and feasible than others. It is therefore essential that decisions on policy options and priorities be taken at the local level. Potential areas of work should be carefully analysed, taking into account factors specific to the locality, region or country. For example, historical, political, cultural, social and economic factors or constraints, existing and available resources, and existing policies and systems need to be taken into account. It is also recognised that prevention and policy implementation are often haphazard, on a case-by-case basis.
The government of the Russian Federation expressed its agreement with the provisions of the who global strategy on nutrition and physical activity and health, recognising its timeliness and relevance.
The national project "health" was launched in Russia on January 1, 2006. As part of the project in 2012, the III all-Russian competition of projects on healthy lifestyle "Healthy Russia"was held. Analysis of the projects showed that most of them were devoted more to tobacco control, rather than aimed at the formation of a healthy diet and physical activity. Also, some of the projects paid attention to the fight against the consequences of obesity, such as cardiovascular diseases and their complications.
In the national project "Health", unfortunately, there is no program to combat obesity and sedentary lifestyles. This is probably due to the fact that in our country obesity is considered as a concomitant disease. For example: "obesity and coronary heart disease", "obesity and hypertension, " obesity and breast cancer", "obesity and metabolic syndrome", "obesity and diabetes", etc. Therefore, there is no accurate statistics of obesity.
It is long overdue to consider obesity as an independent disease. It is the root cause of many diseases and affects many people. It is believed that obesity is a personal problem of a person. No disease is self-medicated on the scale of obesity. For many, excess weight is just something that spoils the figure. Trying to lose weight, people sit on diets, and after a while again gain extra pounds.
The rapidly increasing prevalence of obesity in the Russian Federation requires immediate action, an effective strategy and innovative solutions, the adaptation of existing experience in other countries to the conditions of our country. The prevalence of overweight in the age of 20 + of both sexes according to who data for 2008 in the Russian Federation is 57.8 %.
The Ministry of health and social development of the Russian Federation in the framework of implementation of paragraph 21 of the Order of the Prime Minister of the Russian Federation V. V. Putin dated March 27, 2012 № VP-P12-1763 to organise effective prevention of morbidity and mortality associated with excess body weight, developed the "Provision of medical care to adult population to reduce excess body weight".
The guidelines contain a description of the organisation of medical care for overweight and obese people in primary health care institutions (PHC).
The health of the nation is the highest social value, the basis of national wealth and security of Russia. However, Russians do not tend to take care of their health, think of it as their own resource and capital. This factor is largely key to the dynamics of mortality and morbidity in our country.
Therefore, preventive medicine and the whole society face a difficult task aimed at creating such conditions when it will be beneficial for a person to observe a healthy lifestyle and maintain health for many years.
The creation of so-called “health Schools” in the primary health care system contributes to the solution of this problem. "School of health” is a special form of work with patients. Training programs for "health Schools" are based on active learning and strengthening the patient's ability to plan and develop their own lifelong learning, patient collaboration with each other, and health care provider-patient partnership in health management. Training in these programmes should be part of the consistent training of health workers and can be incorporated into the basic medical education of doctors, nurses and other health workers. Training in the "school" should increase the level of knowledge and practical skills of patients in risk management, contribute to improving the quality of life, preservation and restoration of working capacity. The role of the patient in the treatment of chronic disease can not be limited to passive submission to medical appointments. He should be an active, responsible participant in the therapeutic process, and help him in this can be a medical professional who fully owns the medical knowledge, skills of the organiser, psychologist and teacher.
Classes at the school involve increasing literacy in healthy lifestyles, improving health indicators and quality of life. Nurses with higher education, who have received special training, will take on the teaching function of forming the responsibility for their health in the population. This should contribute to the growth of the professional and organisational-legal status of nursing staff. To streamline this work, it is necessary to enter the code of medical services, reflecting the medical teaching activities in the school of health. Registration of reporting documentation will be an important criterion for targeted funding of nursing staff.
In modern conditions of development of health care and workload of doctors, nurses should take responsibility for the development of preventive education of the population, maintenance of health schools, promotion of healthy lifestyles.
Currently, the role of nursing staff is to use modern technologies, prevention and formation of medical activity of the population in such important areas as a healthy lifestyle, prevention of diseases, poisoning, accidents, sex education, family planning, etc.
Nurses should be aware of the methods of preventive work with the population, methods and techniques to promote a healthy lifestyle, as well as professionally carry out nursing work in hospitals, schools, families, etc.
Such specialists are nurses with higher education in the specialty “Nursing "(qualification " Manager”), and nurses-bachelors.
These specialists are trained to solve problems related to the analysis of the state of health of the population; the organisation and conduct of preventive, recreational activities, the implementation of pedagogical and educational activities.
Conclusion
Obesity is an actual problem of modern society. This is a disease from which everyone is not immune. But you can protect yourself from obesity and other diseases by following a healthy lifestyle. Proper and healthy diet, moderate exercise, maintaining the body in good shape and good sleep will help to keep the body and health in great shape for many years.
Sources
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Overweight
https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/%D0%9E%D0%B6%D0%B8%D1%80%D0%B5%D0%BD%D0%B8%D0%B5
https://zoj.kz/populiarnie/zoj/1947-ozhirenie-problema-sovremennogo-obschestva.html
https://scienceforum.ru/2015/article/2015011209
http://www.medkirov.ru/site/LSP180B0B
http://cgon.rospotrebnadzor.ru/content/62/2977/
https://moluch.ru/archive/202/49559/
http://vapedev.ru/prichiny-ozhireniya/problema-ozhireniya-v-obschestve
https://med.wikireading.ru/65878
https://holesterin.guru/ozhirenie/problema-ozhireniya/
- Особенности перевода текстов официально-делового и научного стилей (Перевод официально-деловых текстов.)
- Практикум по культуре речевого общения (первый иностранный язык)
- Видо-временные формы группы Perfect (Meaning of Perfect Forms)
- Влияние атмосферы магазина на поведение потребителей
- Модели жизненного цикла проекта
- Организационная структура торговли. Организация розничных торговых сетей
- АРХИТЕКТУРА И ОСНОВНЫЕ КОМПОНЕНТЫ ЕСМ-СИСТЕМ
- ДЕЙСТВИЕ ШУМА, УЛЬТРА- И ИНФРАЗВУКА НА ОРГАНИЗМ ЧЕЛОВЕКА В БЫТУ. ОСНОВНЫЕ МЕТОДЫ ЗАЩИТЫ.
- Определение информации и информатизации
- ЭКСПЕРТИЗА ЦЕННОСТИ КОНТЕНТА, ПОРЯДОК ЕЕ ПРОВЕДЕНИЯ
- Школы дизайна
- Основы производственного мастерства ( ФОРМАТЫ БУМАГ И КРИТЕРИИ ИХ ВЫБОРА В ПОЛИГРАФИЧЕСКОМ ПРОИЗВОДСТВЕ)

